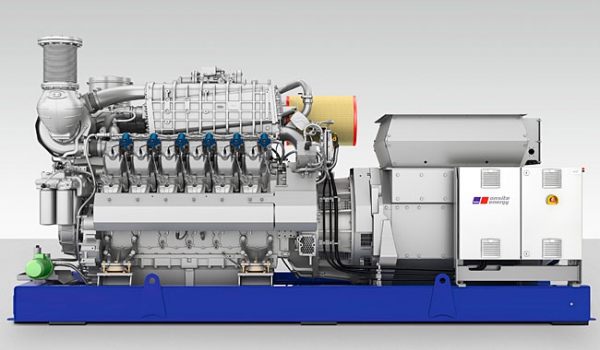
Cogeneration in district heating (CHP for DH) is a solution which provides the Customer with two main products:
- Electricity
- Heat energy in the form of hot water applicable for circulating district heating warm-up as well as for hot water supply
This solution is optimal for the applications where major portion of heat load is in a form of hot water. In this case the heat recovery system of gas reciprocating engine exhaust is executed with application of heat recovery hot water boiler (gas-to -water heat exchanger). Thus, 100% of heat energy generated by gas engine will be produced in the form of hot water.
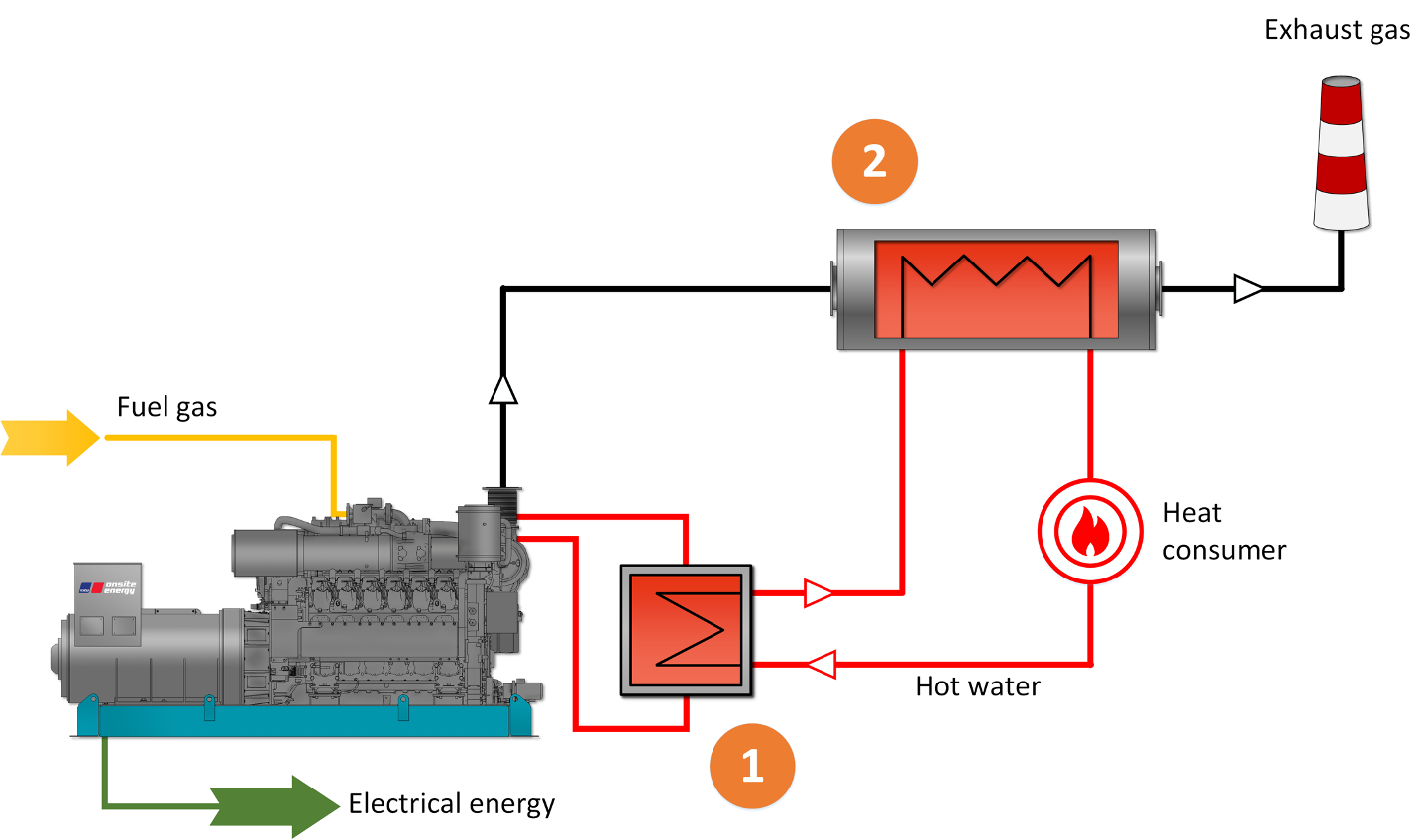
CHP based on gas reciprocating engine therefore has the following heat recovery system operating principle:
- So called low-potential water loop from the engine cooling system can maintain a temperature of incoming hot water at the level of 85/700С. The system hot water flow passes through the separating heat exchanger of the engine cooling system where the heat in turn is taken from the engine core including oil, engine jacket water and fuel mixture cooling;
- Then the system hot water comes to the gas-to-water heat exchanger where it is heated by exhaust gases up to 90-1150С. In the gas-to-water heat exchanger exhaust gases are correspondently cooled from 400-4500С (engine exhaust temperature) to 120 … 1300С (chimney exit temperature) or in some cases with low temperature district heating loop application the exhaust gases are cooled lower till 50C with application of scrubbers or condensers.
- In addition nearly each gas reciprocating engine supply package is provided with an emergency cooling system which includes a dry radiator and a gas-to-water heat exchanger exhaust bypass system which helps keep engines working in emergency modes both with partial and full absence of heat external demand
- Peak shaving | back up additional hot water boilers are integrated into the loop when additional heat demand or particularly essential heat supply security are requested